In today’s rapidly evolving economy, the rise of the gig economy has brought about significant changes in the way people work and conduct business. With more individuals embracing freelance work and entrepreneurship, small businesses in the gig economy play a crucial role in the market. However, navigating the tax landscape can be daunting for these ventures. In this article, we will provide essential tax tips tailored to help small businesses thrive in the gig economy while ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
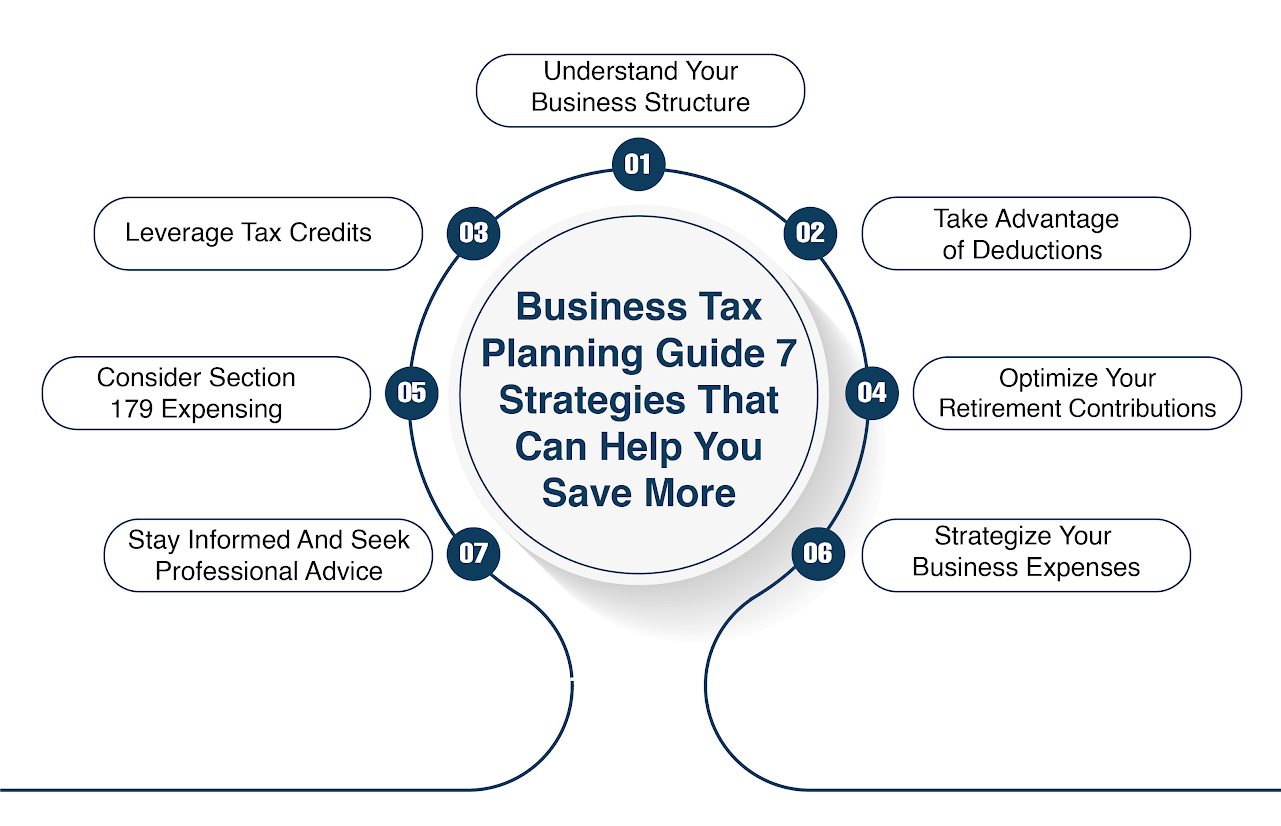
Understand Your Business Structure
Before delving into tax specifics, it’s vital to define your business structure. Common types include sole proprietorship, LLC, and S-corporation. Each structure has its tax implications, and choosing the right one can significantly impact your tax burden. Consult a tax professional to determine the best fit for your business.
Keep Detailed Records
Maintaining accurate and comprehensive records of your income and expenses is critical. Utilize software or apps that simplify the process, ensuring you have a clear overview of your financial transactions. Organized records not only facilitate tax preparation but also serve as valuable insights into your business’s performance.
Understand Tax Deductions
Familiarize yourself with tax deductions applicable to your small business. Common deductions include business-related travel expenses, office supplies, marketing costs, and health insurance premiums. By claiming these deductions, you can reduce your taxable income, ultimately lowering your tax liability.
Quarterly Estimated Tax Payments
As a small business owner in the gig economy, you are likely responsible for making quarterly estimated tax payments to the IRS. Failure to do so may lead to penalties and interest charges. Estimate your tax liability accurately and submit payments regularly to avoid any issues.
Self-Employment Taxes (H2)
In the gig economy, individuals are considered self-employed, subjecting them to self-employment taxes. These taxes encompass both the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. Understanding these obligations is vital for effective tax planning.
Retirement Savings
While running a small business, it’s essential to plan for retirement. Consider opening a tax-advantaged retirement account, such as a SEP-IRA or Solo 401(k). Contributions to these accounts can be deducted from your taxable income, helping you save for the future while reducing your tax burden.
State and Local Taxes
In addition to federal taxes, small businesses in the gig economy must also account for state and local taxes. Different regions may have varying tax rates and requirements. Familiarize yourself with the tax regulations in your specific location to avoid any surprises come tax season.
Utilize Tax Software
Tax software can be a valuable asset for small businesses in the gig economy. It streamlines the tax filing process and ensures accurate calculations. Look for software that caters to self-employed individuals and small businesses to maximize its benefits.
Seek Professional Help
Don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance when it comes to your taxes. Enlisting the services of a qualified tax professional can help you navigate complex tax scenarios, identify potential deductions, and ensure compliance with all tax regulations.
Keep Up with Tax Law Changes
Tax laws are subject to change, and it’s crucial for small business owners in the gig economy to stay informed about these updates. Follow reputable sources for tax news or consult a tax advisor to remain up-to-date with the latest changes that may impact your business.
Separate Personal and Business Finances
Maintain separate bank accounts for personal and business use. This practice ensures clarity when tracking business expenses and income, making tax preparation more manageable and reducing the risk of audits.
Monitor Your Estimated Tax Payments
Regularly assess your estimated tax payments to ensure they align with your actual tax liability. If necessary, adjust your payments to avoid overpaying or underpaying taxes.
Plan for Tax Audits
Though tax audits are rare, they can happen. Be prepared by keeping all supporting documents and receipts organized and readily accessible. Respond promptly and thoroughly to any IRS inquiries if they arise.
Claim all Eligible Credits
Explore available tax credits for small businesses, such as the Small Business Health Care Tax Credit or the Research and Development Tax Credit. These credits can significantly reduce your tax liability.
Conclusion
As the gig economy continues to grow, small businesses operating within it must equip themselves with the knowledge and tools necessary for successful tax management. By understanding their business structure, maintaining detailed records, and staying informed about tax regulations, entrepreneurs can navigate the tax landscape with confidence.
FAQs about Outsourcing Accounting, Payroll, and Finance
Can I deduct my home office expenses as a gig economy worker?
Yes, if you use your home office exclusively and regularly for business purposes, you may be eligible to deduct related expenses, such as utilities and rent.
Is there a threshold for making quarterly estimated tax payments?
If you expect to owe $1,000 or more in taxes for the year, the IRS generally requires you to make quarterly estimated tax payments.
What happens if I miss the deadline for filing my taxes as a small business owner?
Failing to file your taxes on time may result in penalties and interest charges. It’s crucial to file for an extension or submit your tax return as soon as possible.
Can I deduct business-related meals and entertainment expenses?
Yes, you can deduct 50% of qualifying business-related meal and entertainment expenses. Keep detailed records of these expenses, including receipts and the purpose of the expenses.
Do I need to pay taxes on income earned from gig economy platforms like Uber and Airbnb?
Yes, all income earned, including income from gig economy platforms, is subject to taxation. Be sure to report all your income accurately when filing your taxes.